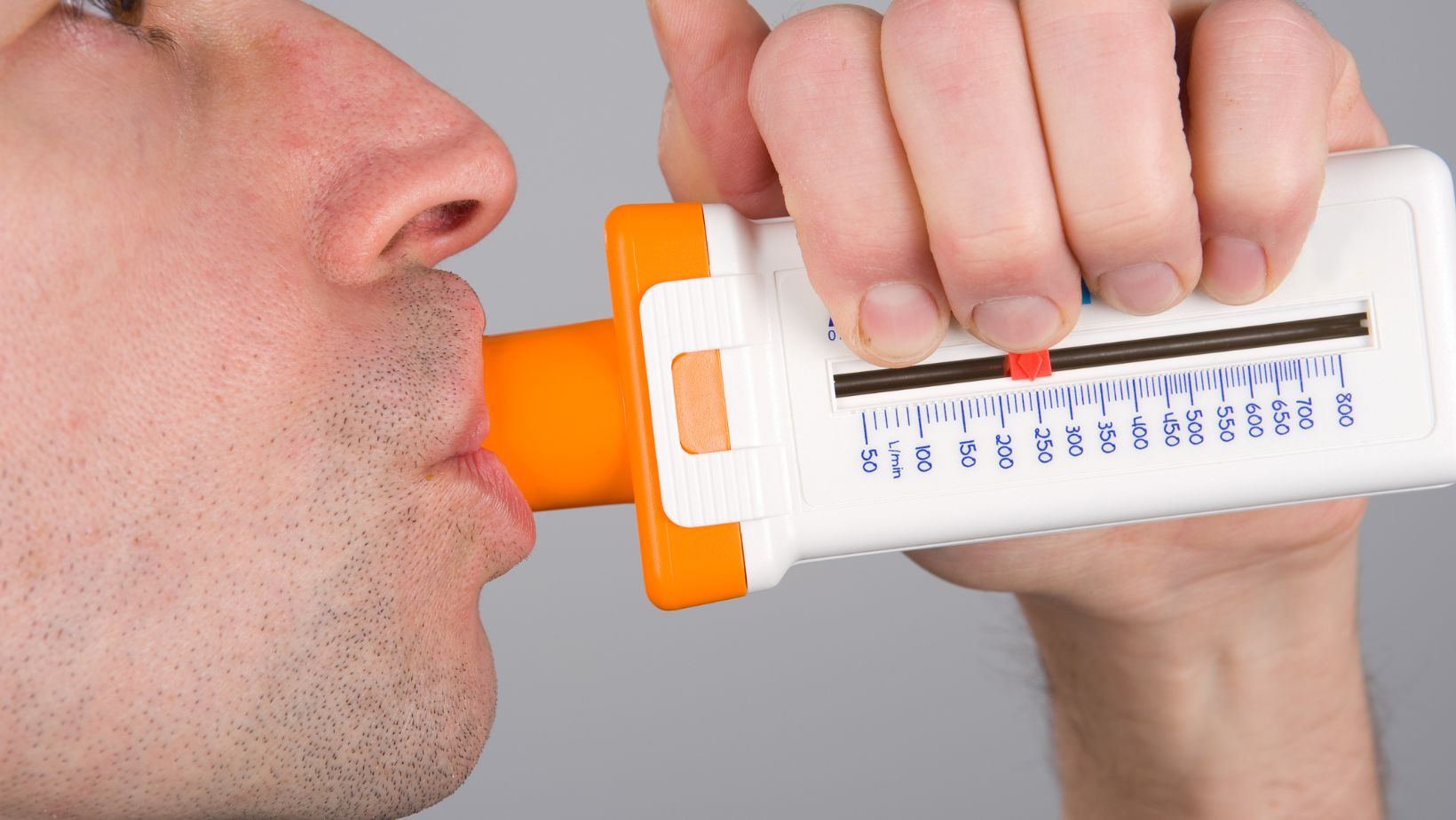
During A Medical Screening, Lung Capacity Testing Is A Standard Procedure
Lung capacity testing is a standard procedure during a medical screening. It plays a crucial role in assessing an individual’s respiratory health and function. By measuring the amount of air a person can inhale and exhale, healthcare professionals gain valuable insights into lung capacity, which can help detect potential issues such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other respiratory conditions.
During this non-invasive test, individuals are asked to take deep breaths and blow forcefully into a device called a spirometer. This simple yet effective tool measures various parameters, including forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). These measurements provide important information about the overall functioning of the lungs and can be used to diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions.
Lung capacity testing is particularly useful for athletes or individuals with physically demanding occupations who require optimal lung function for peak performance. Additionally, it is often recommended for smokers or those with a history of exposure to environmental pollutants, as it helps assess any damage caused by these factors.
Overall, lung capacity testing serves as an essential component of medical screenings by providing valuable data on an individual’s respiratory health. Whether it’s detecting early signs of respiratory conditions or monitoring existing ones, this standard procedure offers valuable insights that aid in diagnosis, treatment planning, and overall patient care.
Read our next page for more lifestyle tips!
The Importance Of Lung Capacity Testing
Lung capacity testing is a fundamental aspect of the medical screening process. During a medical screening, it’s quite common for healthcare professionals to include lung capacity testing as a standard procedure. This test provides valuable insights into an individual’s respiratory health and plays a crucial role in diagnosing various lung conditions.
- Detection of Lung Diseases: Lung capacity testing helps in identifying potential lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary fibrosis. By measuring the amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after taking a deep breath, healthcare providers can evaluate the functioning of the lungs and detect any abnormalities.
- Assessment of Respiratory Fitness: Apart from diagnosing lung diseases, lung capacity testing also allows healthcare professionals to assess an individual’s respiratory fitness level. By comparing the measured results with standardized values based on age, height, and gender, they can determine if an individual has normal or impaired lung function.
- Monitoring Treatment Progress: For individuals already diagnosed with lung conditions, regular lung capacity tests are essential to monitor treatment progress. These tests help healthcare providers evaluate how well prescribed medications or therapies are working and make necessary adjustments if needed.
- Preoperative Evaluation: Prior to undergoing surgery involving general anesthesia, patients may undergo lung capacity testing as part of their preoperative evaluation. This helps ensure that their lungs are healthy enough to tolerate anesthesia and aids in predicting postoperative complications related to breathing.
- Occupational Health Assessments: Certain occupations require individuals to have optimal respiratory function due to exposure to hazardous substances or environments. Lung capacity testing is often included in occupational health assessments to assess whether an individual’s lungs can withstand the demands of their job without compromising their health.
In conclusion, during a medical screening, including lung capacity testing as a standard procedure holds great importance in evaluating respiratory health, detecting lung diseases, monitoring treatment progress, and ensuring individuals are fit for specific occupational requirements. By conducting this simple yet informative test, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care and make informed decisions regarding treatment plans and interventions.





