Still one of the most mysterious and amazing creations found in nature, the human brain is a marvel of biological design. Often referred to as the body’s control center, it arranges the complex symphony of human emotions as well as fundamental survival instincts. How then does brain activity appear and what connection does it have to the emotions we go through?
The Electric Activity: Honoring Neural Activity
The brain basically functions on a series of electrical impulses and chemical messengers. The major cells in the brain, neurons connect at synapses to create intricate networks handling and distributing data.
See neurons as a well-tuned system. Action potentials are electrical bursts produced by neurons activating. These impulses release neurotransmitters that finally bind to receptors in nearby cells via the following axons. This complex process guarantees perfect data flow, which enables us to react to our environment, reason, and emotions.
Brain Colors: Visualizing Neural Activity
Scientists use advanced imaging techniques to examine cerebral activity. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) are two such methods providing access to the inner workings and colors of the brain.
These imaging techniques reveal that different areas of the brain light up in response to various inputs and activity differentially. For instance, the occipital lobe—found at the back of the brain—manages most of the visual information. Looking at a beautiful image, this area becomes really active and shows up as a distinct fMRI scan highlight.
The Spectrum of Emotion: Formation of Feelings
A basic component of the human experience, emotions shape our choices, relationships, and general state of health. When we feel pleased, sad, or furious, however, what occurs in the brain?
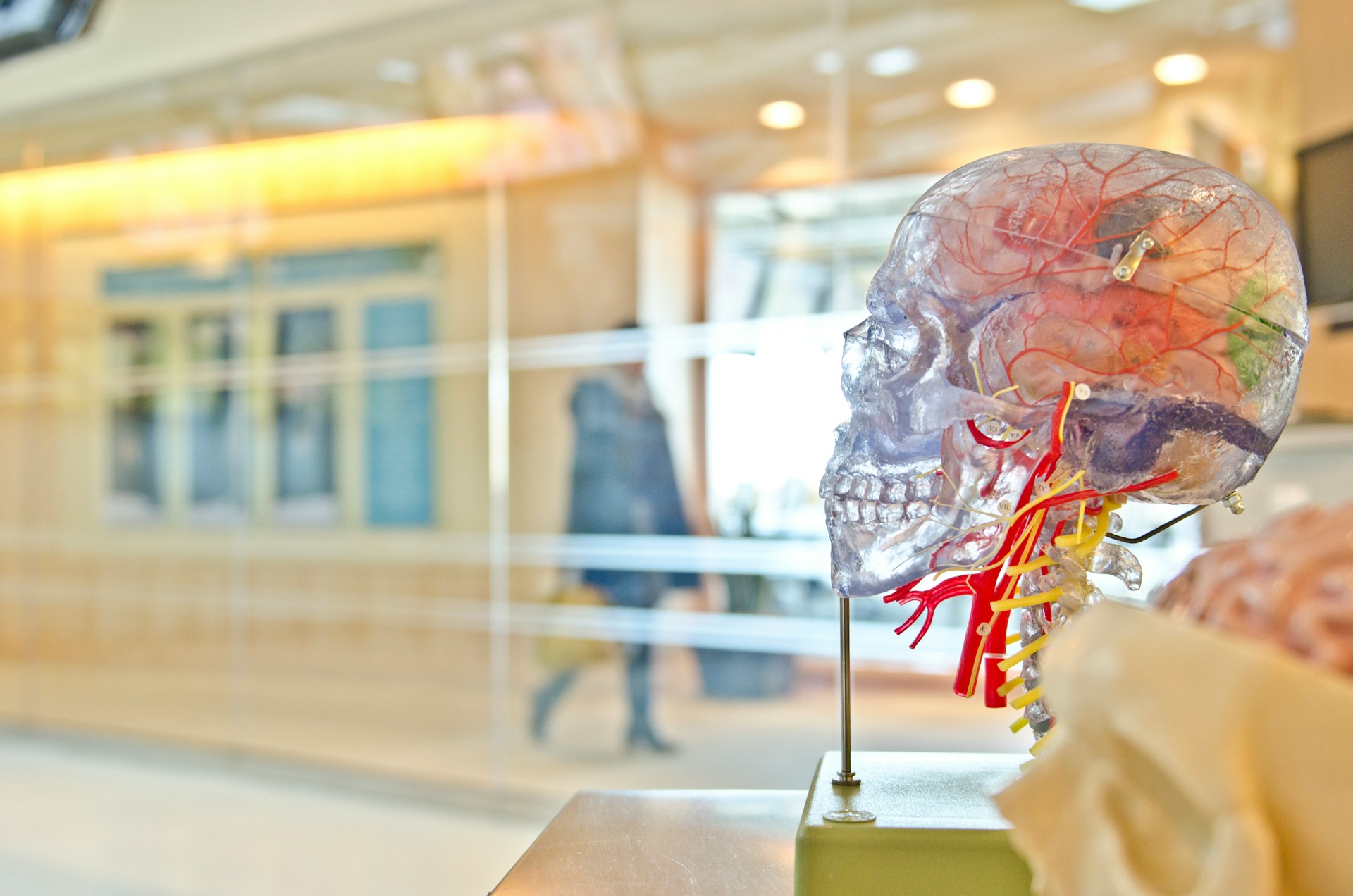
The interplay of several brain areas generates emotions. Often referred to as the emotional core of the brain, the amygdala is absolutely vital in processing pleasure and anxiety. While the prefrontal cortex helps control emotional reactions, the hippocampal forms and retrieves memories.
Important Areas of Brain Function:
· Amygdala: Oversees feelings like pleasure, wrath, and terror.
· The hippocampal is involved in memory development and retrieval.
· Regulation of emotional reactions and decision-making occurs in the prefrontal cortex.
The Emotional Palette Depends on the Colors
Apart from learning the color of the brain and its activity, knowing how colors affect us is also pivotal. Fascinatingly, colors themselves may have a strong emotional effect on us. Called color psychology, this phenomenon investigates how various colors influence human behavior and emotions.
Warm colors like red and orange, for example, are often connected with energy and enthusiasm; cold colors like blue and green tend to inspire peace and relaxation. The way the brain responds to color is influenced by both biological elements and cultural links, which shape everything from home design to clothes selections.






